ALBA simplifies PCB Power & Thermal management
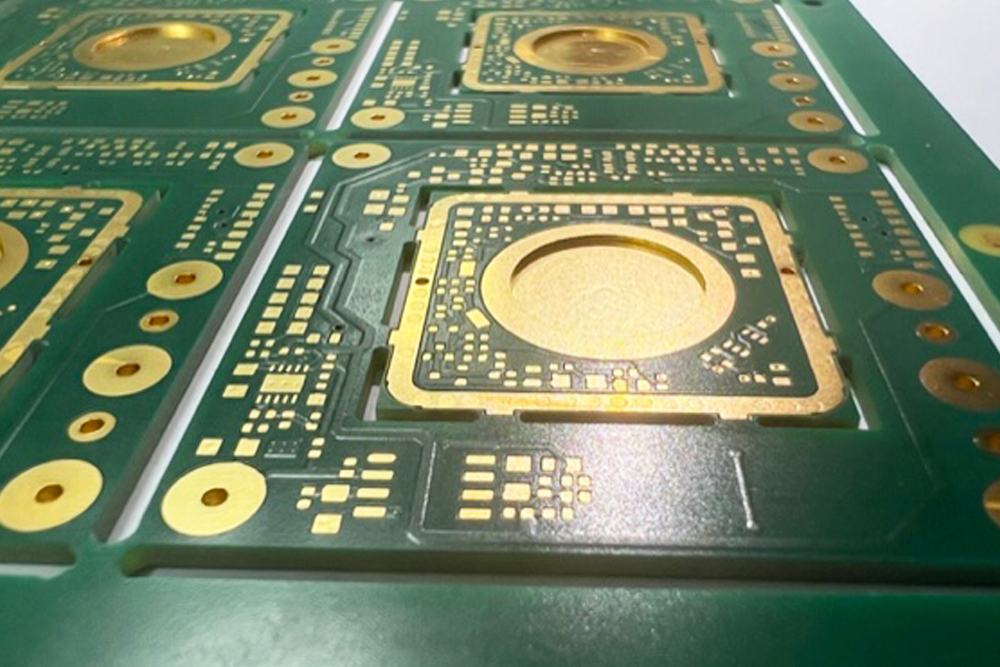
Technologies to improve heat dissipation and high current management in PCBs are constantly evolving to meet the needs of increasingly complex applications. The ALBA group is able to offer a wide range of technical solutions to solve these problems, especially when it is desired to combine a digital part with very stringent parameters (QFN micro-components, BGA, layout with reduced width of conductors, and low electrical gaps between the conductors themselves) with a purely power part of the pcb that requires copper thickness over 70um (up to 3mm for example) so as to be able to withstand high amperages and complex thermal management.
In particular:
BBE PCBs (Bus Bars Embedded)
Printed circuit boards with integrated bus bars feature strips or bars of conductive materials embedded in one or more layers of the PCB that can be made in various shapes, thicknesses and sizes depending on the specific needs of the project. They have the function of connecting different points of the circuit by managing very high currents, without incurring thermal excesses due to the joule effect and without having to implement particular precautions aimed at thermal management of the PCB.
This technical solution can also significantly reduce the overall size of the electronic devices by eliminating the installation of other external conductive elements. It is also possible to make BBs that protrude from the profile of the pcb, so that they can be connected directly by power terminals to a thick high current metal wires.
BBE technology is used for a wide range of applications, such as electric vehicle power and charging systems, DC/DC converters and LED lighting devices.
ECC PCBs (Embedded Copper Coin)
Always taking advantage of the metal embedded technology, and taking into account that the thermal stress due to the operation of the boards at high temperatures is one of the main causes of malfunctioning of the power devices, especially if made with printed circuits with a high integration density, it is possible to apply embedded on the printed circuit a metal inserts (copper) of considerable thickness (in the order of millimetres) positioned on the dissipation areas of the power components: these inserts are generally indicated as COINs: components such as the MOSFET transistors can therefore be directly soldered onto these inserts allowing an easier thermal management than not applying a generic design of a dissipative pad with or without the presence of thermal vias. The high temperatures reached by these power components in fact require the PCBs that receive them to guarantee an effective transfer and distribution of the energy heat generated during their functionality both to the ground planes present on the printed circuit itself and to the external dissipation surfaces (which are then coupled with additional heat sinks).
Printed circuits with these „coins” therefore incorporate solid copper elements of small dimensions (typically the same as the dissipation pad of the power component concerned) and considerable thickness (even as thick as the pcb) which have the function of transmitting heat through the circuit section. The shape of these inserts can be rectangular but also shaped according to need (for example for banks of mosfets in parallel or in sequence). Their profile could have lips of different thickness to allow the passage of conductors not connected to them (high digital design). In the same way they can be machined mechanically to have hollow surfaces with respect to the surface of the printed circuit which integrates them.
This technology is often used to improve thermal management in designs where there are specific localized areas with elevated temperatures by providing a heat sink integrated into the PCB, but it can also be combined to increase the distributable electric current within the PCB by combining the technology integrated bus bars. ECC circuits are often used in automotive, medical and new generation telecom/datacom infrastructure applications, but also on high power PCBs in the industrial world.
In conclusion, the integration of „bus bars” or „coins” in printed circuits represent advanced and innovative technological solutions that offer many advantages over traditional PCBs in terms of reliability, performance, space and overall cost of electronic devices.
Inne posty

10 reasons why Alba PCB Group can satisfy all your requests.
Alba PCB Group is an international group, its headquarter located in Italy, composed by highly...
Przeczytaj więcej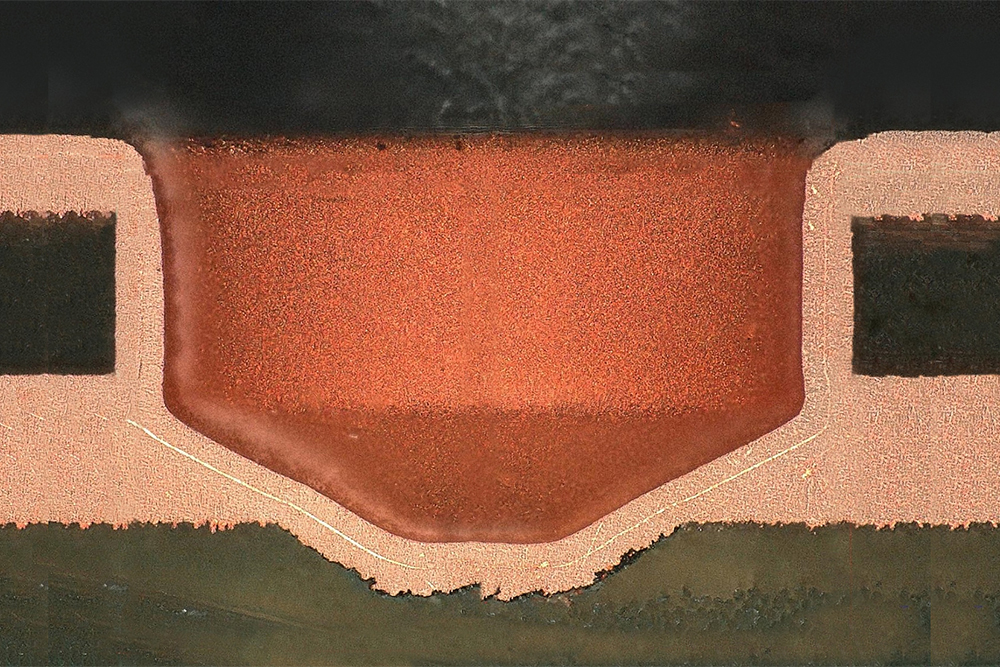
Using blind vias in PCBs avoiding criticalities
Guidelines for using blind vias. BLIND VIAS AND CONSTRUCTION PARAMETERS Blind vias are plated-through...
Przeczytaj więcej
Checking quality looking “2000 times” more!
We don’t take our eyes off from quality! Our control department is the place where...
Przeczytaj więcej