Reduce the ionic contamination of PCBs.
15% of the anomalies on the electronic boards are caused by ionic residues.
The ionic contamination of the boards themselves, even before the printed circuits that they support are contaminated, is due to a set of polluting agents that remain after the production processes of the circuit itself: generic salts, organic and inorganic acids, ethanolamines, flux activators, and chemical agents derived from the processes of metal plating, human sweat.
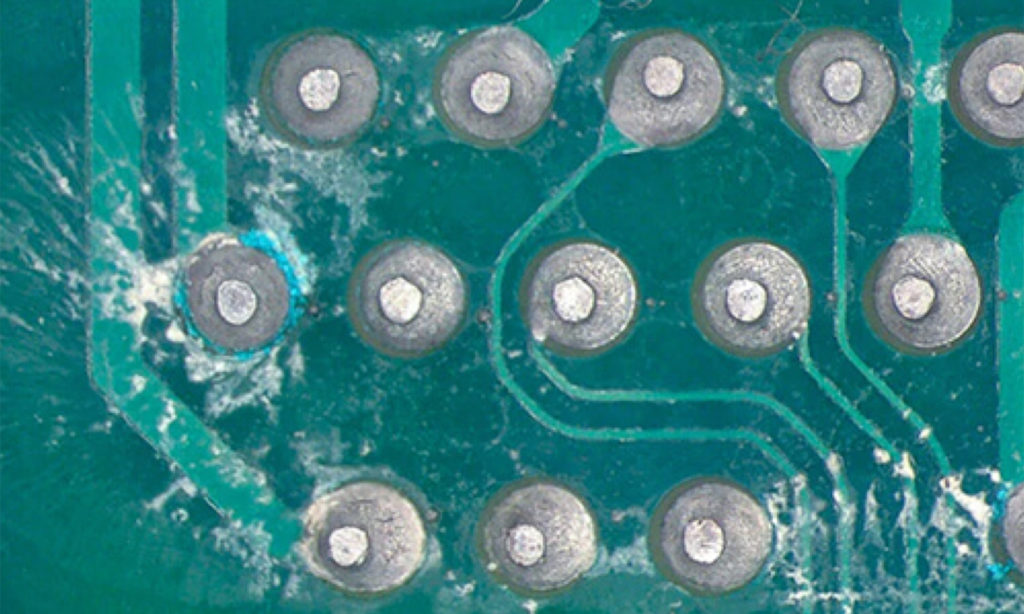

Under certain environmental or usage conditions these residues can dissolve in a water/alcohol solution, and become conductive, thus creating defects that undermine the reliability of the board over time and cause:
• Corrosion, that weakens the metal conductors (tracks and pads);
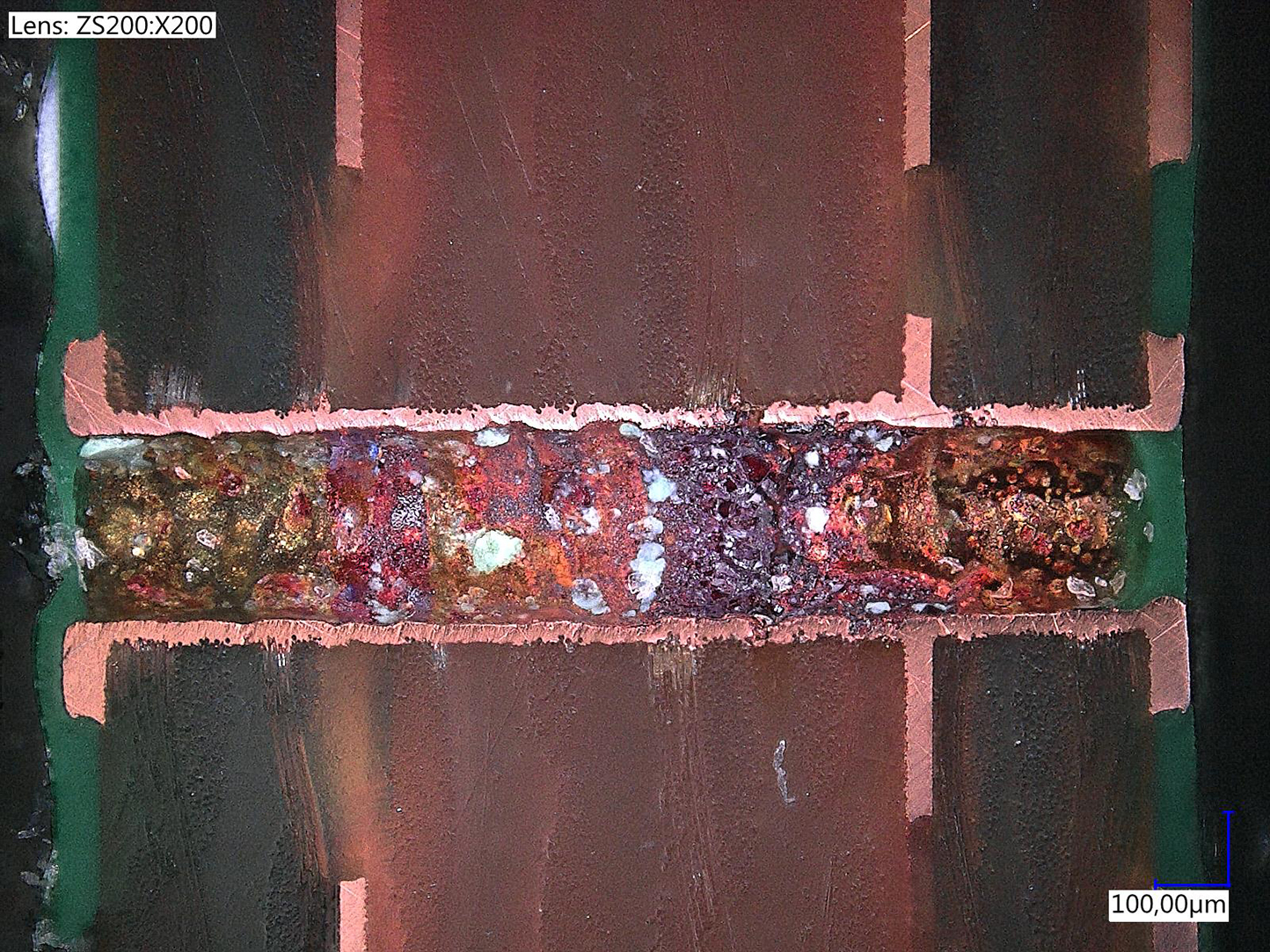

• Formation of dendrites and loss of insulation, that can lead to short circuits;
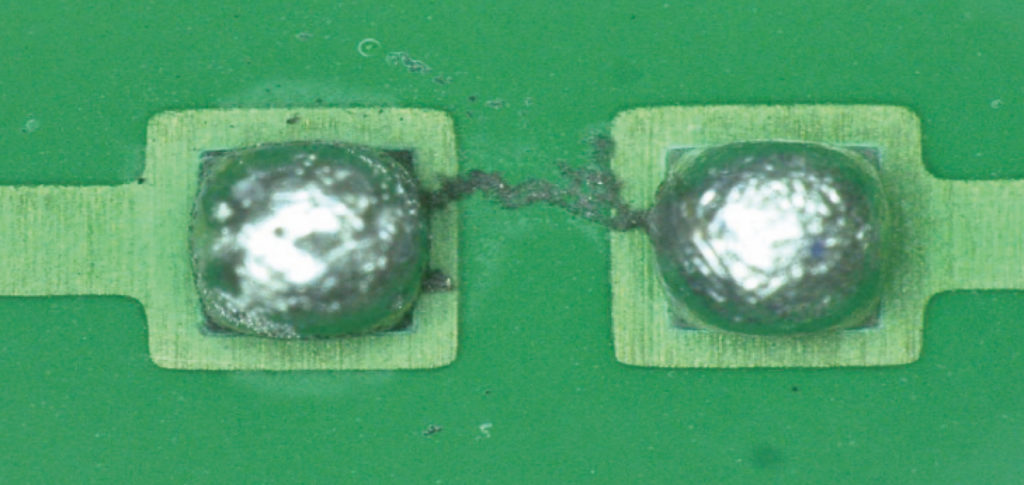
• Electrochemical migration, another cause of short circuits;
• Electrical leakage, that leads to the boards not working properly
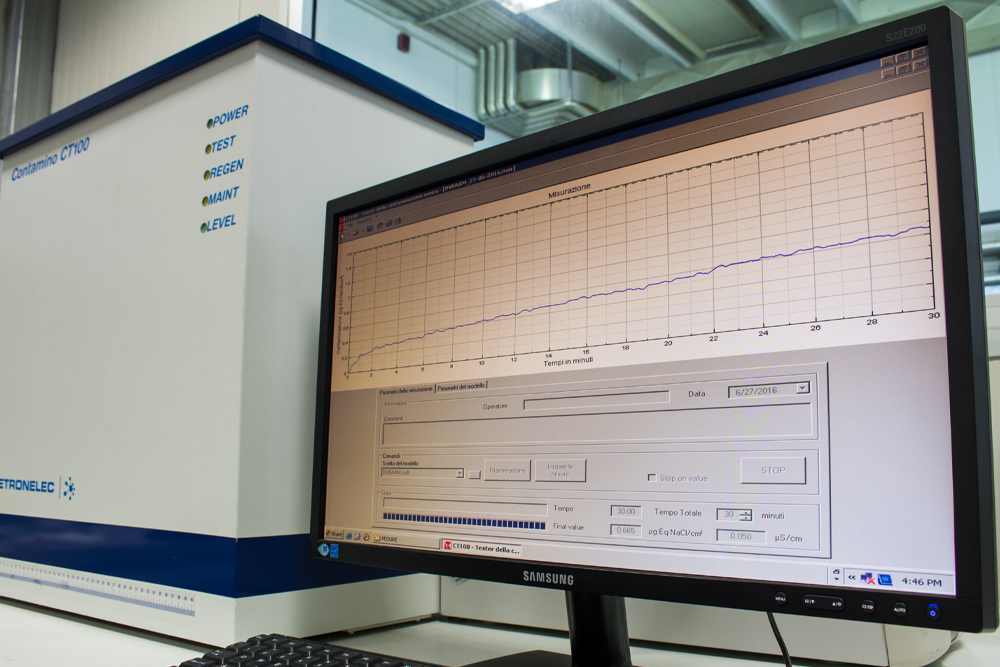
In order to avoid all of this and always deliver a highly reliable printed circuit, the Alba PCB Group has adopted a specific internal procedure, which, through the use of the most recent generation of ionograph, allows a rapid evaluation of ionic contamination.
Examination is conducted constantly on:
• the productive process;
• the lots produced;
• lots produced that come from areas outside the EEC.
Other Posts
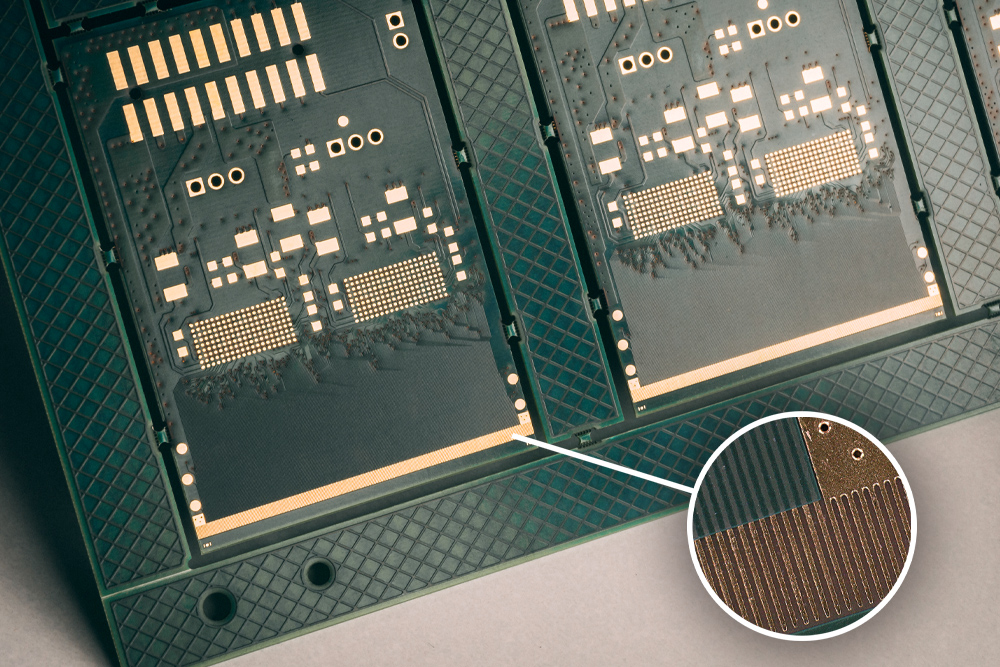
A PCB on the edge of microelectronics
0.11 mm step connector: 70 micron track, 40 micron insulation. The possibility of creating a...
READ ALL
The new shadow line for a perfect metallization of micro- and blind holes
Fifteen meters of automatic horizontal line for removing all the impurities from the holes, making...
READ ALL
Alba PCB Group expands into Germany
Acquires Q-print electronic GmbH Acquiring the majority share in Q-Print electronic Gmbh, a German company...
READ ALL